FastAPI讲解
一.FastAPI是什么
FastAPI 是一个用于构建 API 服务的高性能 web 框架。
需要使用 Python 3.6+,基于标准的 Python 类型提示。
1.关键特性
- 快速:可与 NodeJS 和 Go 比肩的极高性能(归功于 Starlette 和 Pydantic),是最快的 Python web 框架之一。
- 高效编码:提高功能开发速度约 200% 至 300%。
- 更少 bug:减少约 40% 的人为错误(开发者导致)。
- 智能:极佳的编辑器支持。处处皆可自动补全,减少调试时间。
- 简单:设计的易于使用和学习,阅读文档的时间更短。
- 简短:使代码重复最小化。通过不同的参数声明实现丰富功能。bug 更少。
- 健壮:生产可用级别的代码。还有自动生成的交互式文档。
- 标准化:基于(并完全兼容)API 的相关开放标准:OpenAPI (以前被称为 Swagger) 和 JSON Schema。
二.安装启动
技术背景:Py3.6+,Starlette,Pydantic
1.安装插件fastapi
pip install fastapi2.安装启动插件
pip install uvicorn3.启动服务
# main指的文件名,若文件名为fastapi,则为 uvicorn fastapi:app --reload --port 5000 --host 0.0.0.0
uvicorn main:app --reload --port 5000 --host 0.0.0.0FastAPI 推荐使用 uvicorn 来运行服务,Uvicorn 是基于uvloop 和 httptools 构建的闪电般快速的 ASGI 服务器。
uvicorn main:app 指的是:
- main:文件main.py
- app: 创建的启用对象
- --reload: 热启动,方便代码的开发,指检测到文件改动时自动重载(这在调试时非常有用)
- --port 端口
- --host 访问ip
三.简单实例
1.路径参数和查询参数
在根目录创建项目文件main.py:
from fastapi import FastAPI
app = FastAPI()
# 定义一个路径操作装饰器
@app.get("/")
def read_root():
return {"我的第一个FastAPI": "Hello World!"}
@app.get("/test/{use_id}")
def read_item(use_id: int, key: str = None):
return {"use_id": use_id, "key": key}说明:
- url:
/和/test/{use_id}两个url都可以接收HTTP请求。 /和/test/{use_id}都采用GET方式的HTTP请求方法。/test/{use_id}包含路径参数use_id,类型为int。/test/{use_id}还包含一个可选的参数key,类型为str, 默认为null。声明不属于路径参数的其他函数参数时,它们将被自动解释为"查询字符串"参数 查询字符串是键值对的集合,这些键值对位于 URL 的 ? 之后,并以 & 符号分隔 例如: http://0.0.0.0:5000/test/123?key=111- 如果
/test/{use_id}没给默认值,且也不传参数过来,会报错:
{"detail":[{"loc":["query","key"],"msg":"field required","type":"value_error.missing"}]}测试
- 请求
/接口,没有传参:
http://0.0.0.0:5000/
{"我的第一个FastAPI":"Hello World!"}
# curl
curl http://0.0.0.0:5000/
{"我的第一个FastAPI":"Hello World!"}- 请求
/test/{use_id}接口,传参(路径参数)
http://0.0.0.0:5000/test/123
{"use_id":123,"key":null}
# curl
curl http://0.0.0.0:5000/test/123
{"use_id":123,"key":null}- 请求
/test/{use_id}接口,传参(路径参数,查询参数)
http://0.0.0.0:5000/test/123?key=111
{"use_id":123,"key":"111"}
#curl
curl 'http://0.0.0.0:5000/test/123?key=111'
{"use_id":123,"key":"111"}2.路径参数预定义操作
如果想对路径参数做一个预定义,可以使用Enum(枚举):
from enum import Enum
from fastapi import FastAPI
class ModelName(str, Enum):
add = "add"
update = "update"
delete = "delete"
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/model/{model_name}")
async def get_model(model_name: ModelName, key: str = None):
if model_name == ModelName.add:
return {"model_name": model_name, "message": "这是添加操作!", "key": key}
if model_name.value == "update":
return {"model_name": model_name, "message": "这是更新操作!", "key": key}
return {"model_name": model_name, "message": "这是删除操作!", "key": key}测试结果
curl 'http://0.0.0.0:5000/model/add'
{"model_name":"add","message":"这是添加操作!","key":null}
curl 'http://0.0.0.0:5000/model/update'
{"model_name":"update","message":"这是更新操作!","key":null}
curl 'http://0.0.0.0:5000/model/delete'
{"model_name":"delete","message":"这是删除操作!","key":null}
以上例子就会限定每次传进来的参数,如果不是枚举类里面的预设值将会报错:
curl 'http://0.0.0.0:5000/model/1111'
{"detail":[{"loc":["path","model_name"],"msg":"value is not a valid enumeration member; permitted: 'add', 'update', 'delete'","type":"type_error.enum","ctx":{"enum_values":["add","update","delete"]}}]}3.获取查询参数
data_dict = [{'item': '01', 'name': 'one'}, {'item': '02', 'name': 'two'}, {'item': '03', 'name': 'three'},
{'item': '04', 'name': 'four'}, {'item': '05', 'name': 'five'}]
@app.get('/data')
async def get_data(start_indx: int = 0, step: int = 5):
return data_dict[start_indx: start_indx + step]调用结果
# 默认数据
curl http://0.0.0.0:5000/data
[{"item":"01","name":"one"},{"item":"02","name":"two"},{"item":"03","name":"three"},{"item":"04","name":"four"},{"item":"05","name":"five"}]# 查询指定数据
curl 'http://0.0.0.0:5000/data?start_index=0&step=2'
[{"item":"01","name":"one"},{"item":"02","name":"two"}]4.body传参
针对Body传参的情况, 其实也是以函数传参的形式, 但是考虑到传统的 form-data 传参方式字段很多, 可以采用 application/json 的方式, 并且定义一个参数类来管控参数。
from fastapi import FastAPI
from pydantic import BaseModel
class Item(BaseModel): # 定义一个类用作参数
name: str
age: int
height: float
is_offer: bool = None # 该字段可为空
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/{people_id}")
async def update_item(people_id: str, item: Item): # item需要与Item对象定义保持一致
return {
"method": 'get',
"people_name": item.name,
"people_age": item.age,
"people_height": item.height,
'people':people_id
}
@app.put("/{people_id}")
async def update_item(people_id: str, item: Item): # item需要与Item对象定义保持一致
return {
"method": 'put',
"people_name": item.name,
"people_age": item.age,
"people_height": item.height,
'people':people_id
}
@app.post("/{people_id}")
async def update_item(people_id: str, item: Item): # item需要与Item对象定义保持一致
return {
"method": 'post',
"people_name": item.name,
"people_age": item.age,
"people_height": item.height,
'people':people_id
}
@app.delete("/{people_id}")
async def update_item(people_id: str, item: Item): # item需要与Item对象定义保持一致
return {
"method": 'delete',
"people_name": item.name,
"people_age": item.age,
"people_height": item.height,
'people':people_id
}4.1 postman测试
GET请求:
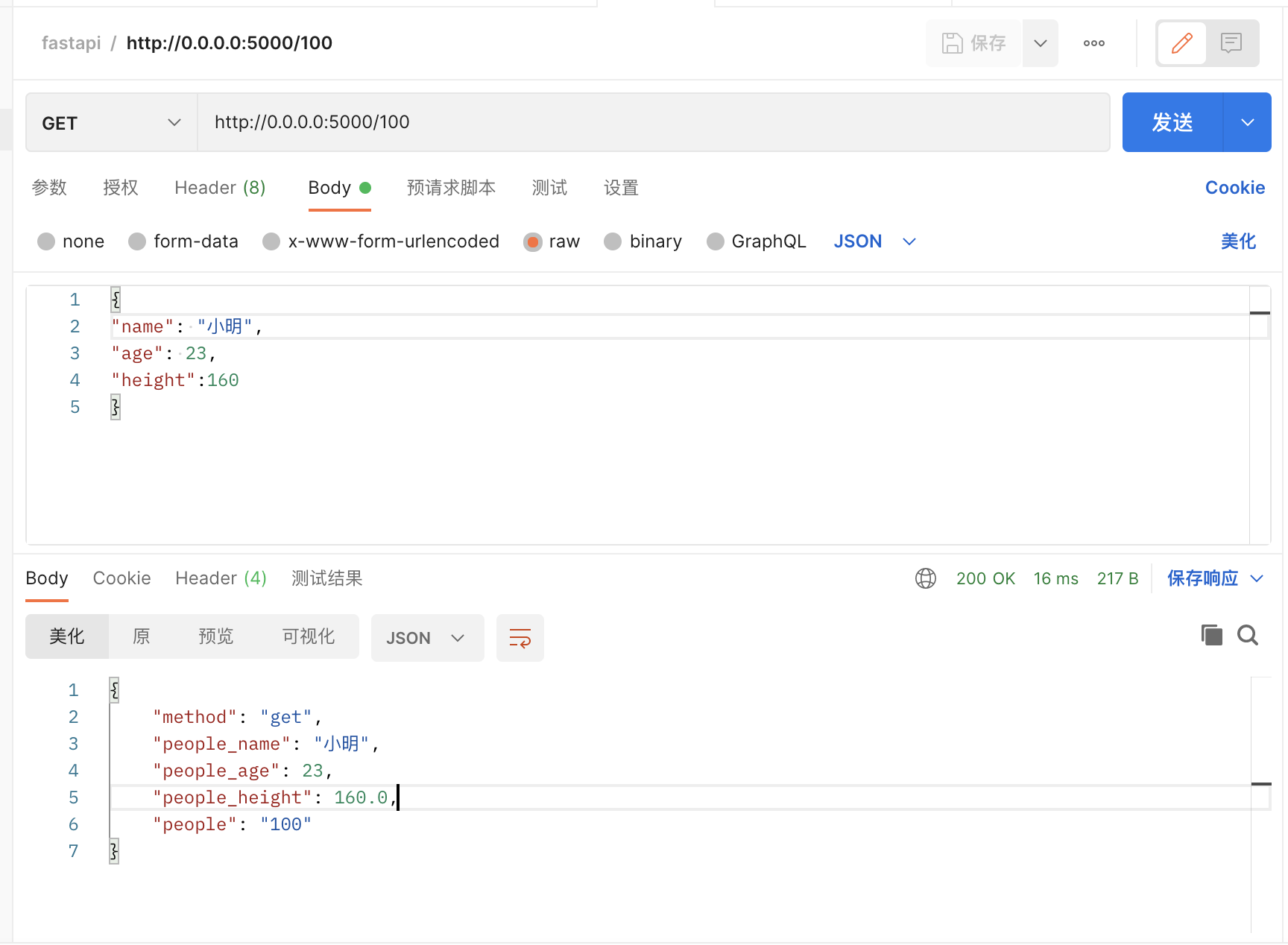
http://0.0.0.0:5000/100
# body
# json
{
"name": "小明",
"age": 23,
"height":160
}
# curl http://0.0.0.0:5000/100
curl -H "Content-Type:application/json" -X GET --data '{"name": "小明","age": 23,"height":160}' http://0.0.0.0:5000/100
{"method":"get","people_name":"小明","people_age":23,"people_height":160.0,"people":"100"}结果
{
"method": "get",
"people_name": "小明",
"people_age": 23,
"people_height": 160.0,
"people": "100"
}PUT请求:
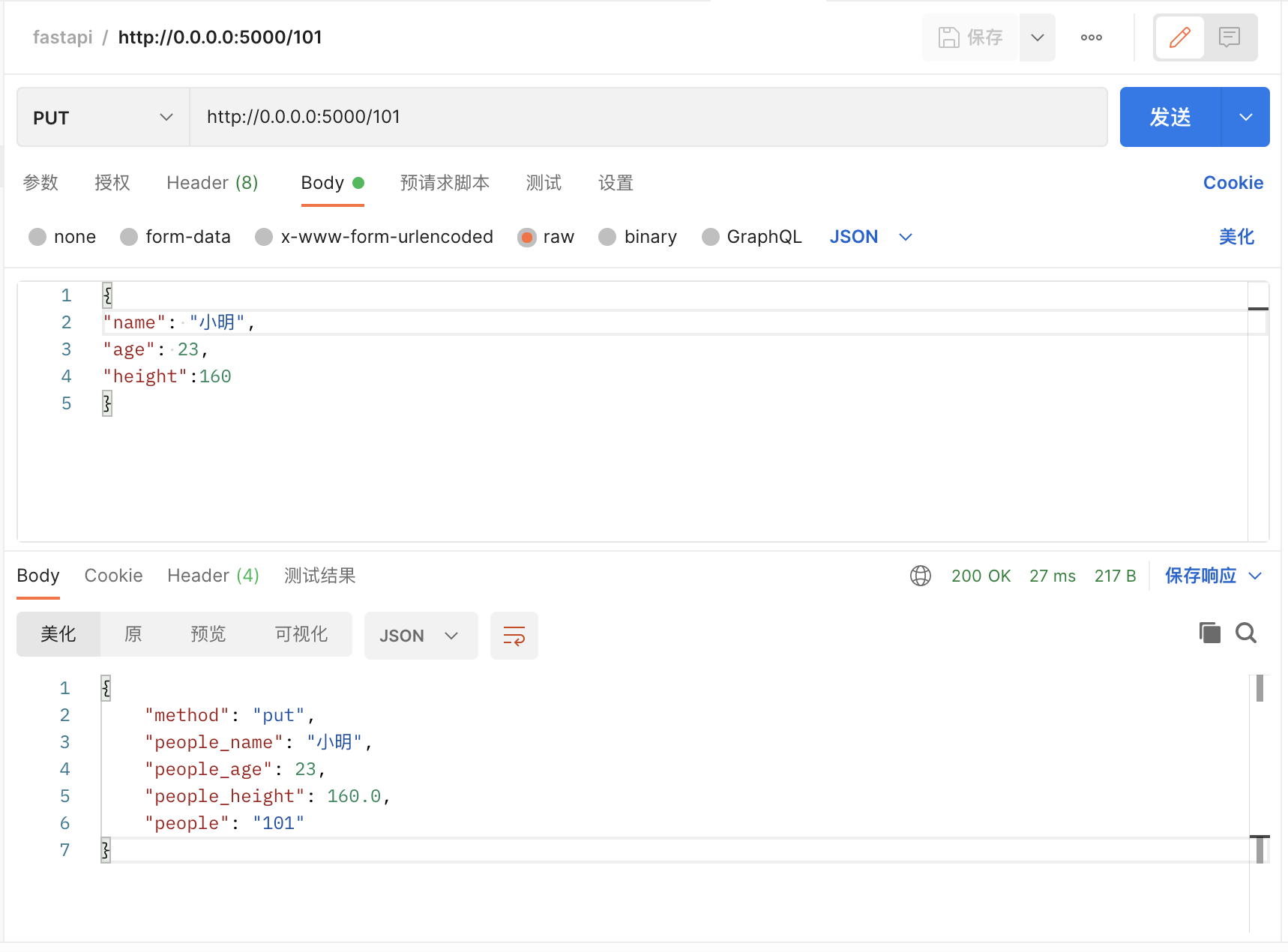
http://0.0.0.0:5000/101
# body
# json
{
"name": "小明",
"age": 23,
"height":160
}
curl -H "Content-Type:application/json" -X PUT --data '{"name": "小明","age": 23,"height":160}' http://0.0.0.0:5000/101
{"method":"put","people_name":"小明","people_age":23,"people_height":160.0,"people":"101"}{
"method": "put",
"people_name": "小明",
"people_age": 23,
"people_height": 160.0,
"people": "101"
}POST请求:
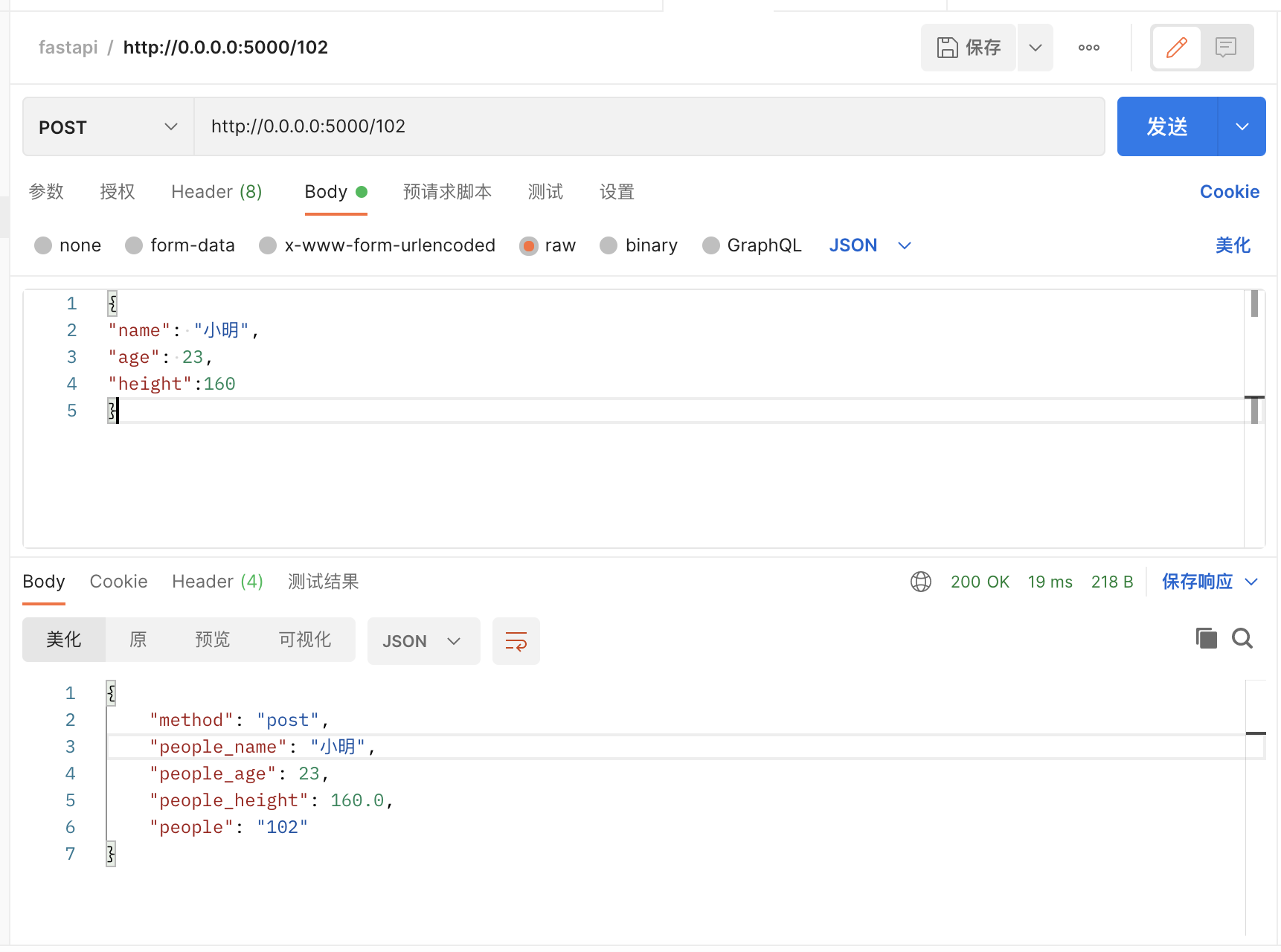
curl -H "Content-Type:application/json" -X POST --data '{"name": "小明","age": 23,"height":160}' http://0.0.0.0:5000/102
{"method":"post","people_name":"小明","people_age":23,"people_height":160.0,"people":"102"}DELETE请求:
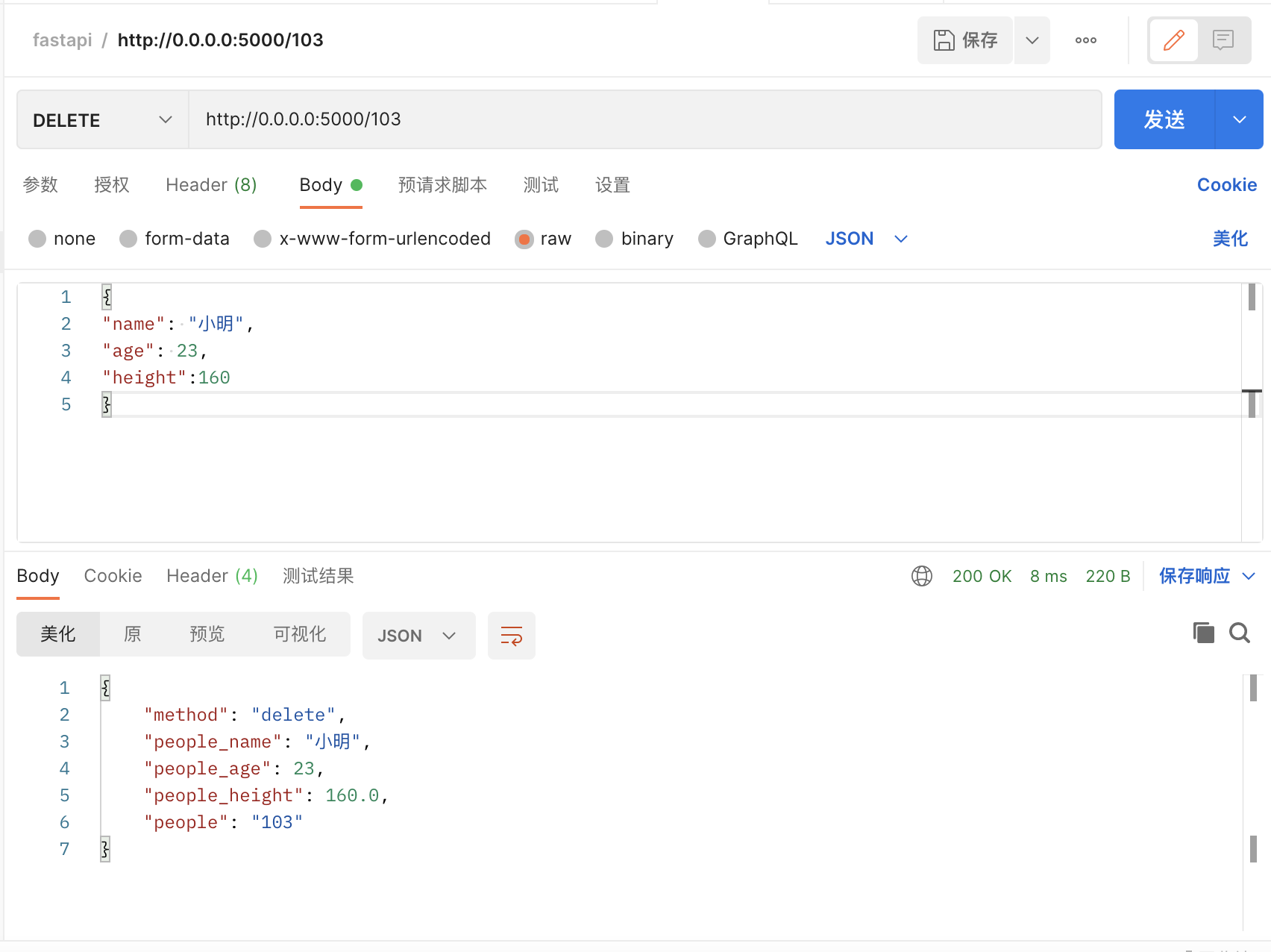
curl -H "Content-Type:application/json" -X DELETE --data '{"name": "小明","age": 23,"height":160}' http://0.0.0.0:5000/102
{"method":"delete","people_name":"小明","people_age":23,"people_height":160.0,"people":"102"}四.自动生成接口文档
FastApi 会自己给你生成接口文档, 真正的解放你的双手
FastApi 默认提供了两种接口文档, 其实内容一样, 只是使用了两个开源的文档框架
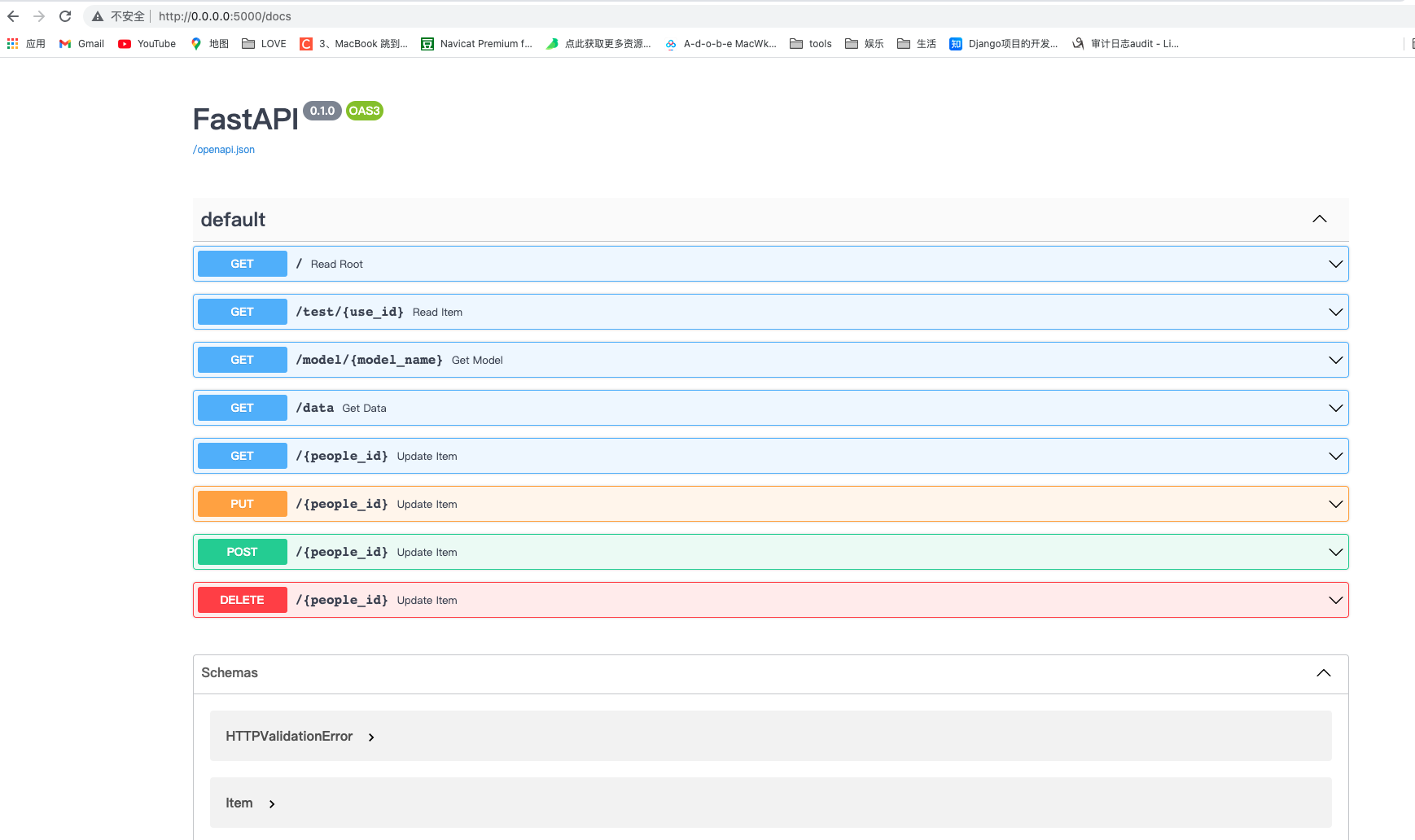
1. swagger
默认的文档位置在 http://127.0.0.1:5000/docs 使用浏览器打开即可
在你更新代码时接口文档也会同步更新
如下图:
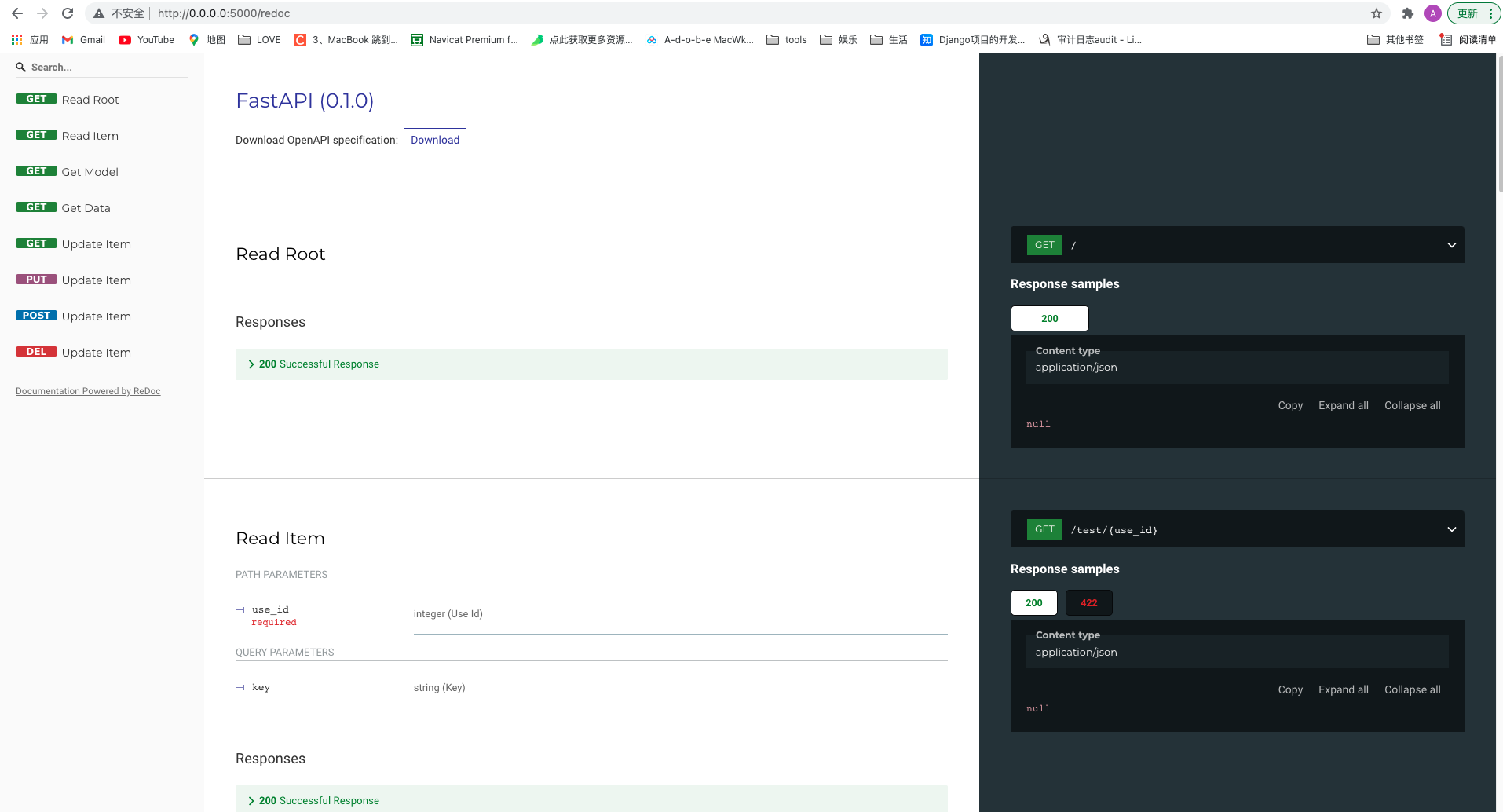
2. redoc
默认的文档位置在 http://127.0.0.1:5000/redoc 使用浏览器打开即可
在你更新代码时接口文档也会同步更新
如下图:
五.RESTful接口规范之GET/POST/PUT/DELETE
REST 是Representational State Transfer的缩写,翻译是"表述性状态转移".
面向资源是REST最明显的特征,对于同一个资源的一组不同的操作。
资源是服务器 上一个可命名的抽象概念,资源是以名词为核心来组织的,首先关注的是名词。
REST要求,必须通过统一的接口来对资源执行各种操作。
对于每个资源只能执行一组有限的操作。
7个HTTP方法:GET/POST/PUT/DELETE/PATCH/HEAD/OPTIONS
如果按照HTTP方法的语义来暴露资源,那么接口将会拥有安全性和幂等性的特性,例如GET和HEAD请求都是安全的, 无论请求多少次,都不会改变服务器状态。而GET、HEAD、PUT和DELETE请求都是幂等的,无论对资源操作多少次, 结果总是一样的,后面的请求并不会产生比第一次更多的影响。
GET,DELETE,PUT和POST的典型用法
1. GET
安全且幂等
表示获取
200(OK) - 表示已在响应中发出
204(无内容) - 资源有空表示
301(Moved Permanently) - 资源的URI已被更新
303(See Other) - 其他(如,负载均衡)
304(not modified)- 资源未更改(缓存)
400 (bad request)- 指代坏请求(如,参数错误)
404 (not found)- 资源不存在
406 (not acceptable)- 服务端不支持所需表示
500 (internal server error)- 通用错误响应
503 (Service Unavailable)- 服务端当前无法处理请求2. POST
不安全且不幂等
使用服务端管理的(自动产生)的实例号创建资源
创建子资源
200(OK)- 如果现有资源已被更改
201(created)- 如果新资源被创建
202(accepted)- 已接受处理请求但尚未完成(异步处理)
301(Moved Permanently)- 资源的URI被更新
303(See Other)- 其他(如,负载均衡)
400(bad request)- 指代坏请求
404 (not found)- 资源不存在
406 (not acceptable)- 服务端不支持所需表示
409 (conflict)- 通用冲突
412 (Precondition Failed)- 前置条件失败(如执行条件更新时的冲突)
415 (unsupported media type)- 接受到的表示不受支持
500 (internal server error)- 通用错误响应
503 (Service Unavailable)- 服务当前无法处理请求3. PUT
不安全但幂等
通过替换的方式更新资源
如果未被修改,则更新资源(乐观锁)
200 (OK)- 如果已存在资源被更改
201 (created)- 如果新资源被创建
301(Moved Permanently)- 资源的URI已更改
303 (See Other)- 其他(如,负载均衡)
400 (bad request)- 指代坏请求
404 (not found)- 资源不存在
406 (not acceptable)- 服务端不支持所需表示
409 (conflict)- 通用冲突
412 (Precondition Failed)- 前置条件失败(如执行条件更新时的冲突)
415 (unsupported media type)- 接受到的表示不受支持
500 (internal server error)- 通用错误响应
503 (Service Unavailable)- 服务当前无法处理请求4. DELETE
不安全但幂等
删除资源
200 (OK)- 资源已被删除
301 (Moved Permanently)- 资源的URI已更改
303 (See Other)- 其他,如负载均衡
400 (bad request)- 指代坏请求
404 (not found)- 资源不存在
409 (conflict)- 通用冲突
500 (internal server error)- 通用错误响应
503 (Service Unavailable)- 服务端当前无法处理请求